
- #DOCKER REMOVE CONTAINER ALL UPDATE#
- #DOCKER REMOVE CONTAINER ALL CODE#
- #DOCKER REMOVE CONTAINER ALL DOWNLOAD#
Only clean up container images that have been created over 24 hours ago runĭocker image prune -a –filter "until=24h" If you want to clean up and delete all unused container images, just add -a Its a pretty safe command to clean up your local filesystem The first command is used to remove local container images that are not used by any container and are not tagged. Get docker container disk utilization: docker system df Get docker container including size: docker ps -s bash shell with root if container is running in a different user context docker exec -i -t -u root /bin/bash.bash shell into container docker exec -i -t /bin/bash – if bash is not available use /bin/sh.
#DOCKER REMOVE CONTAINER ALL UPDATE#
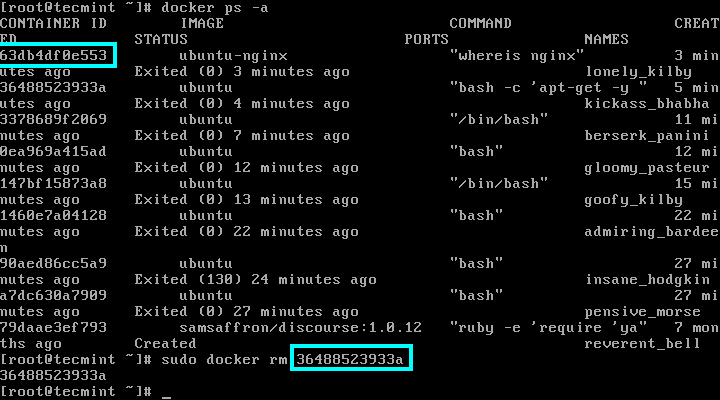
update and stop a container that is in a crash-loop with docker update –restart=no & docker stop. delete all images with docker rmi $(docker images -q). delete all stopped containers with docker rm $(docker ps -a -q). kill all running containers with docker kill $(docker ps -q). to copy /etc/file to your current directory. docker cp to copy files from a running container to the host or the way around. docker update –restart=no updates container policies, that is especially helpful when your container is stuck in a crash loop. docker start – starts a stopped container using the last state. docker stop mycontainer stops one container, while docker stop $(docker ps -a -q) stops all running containers. docker stop stops one or more containers. docker rmi myimage, but make sure no running container is based on that image docker rmi removes one or more images. 
docker rm mycontainer, but make sure the container is not running
docker rm removes one or more containers. That enables container communication by simple container name instead of IP. docker network connect adds the container to the given container network. docker network ls – list all networks available for docker container. docker volume ls lists the volumes, which are commonly used for persisting data of Docker containers. 
To continue showing log updates just use docker logs -f mycontainer
docker logs display the logs of a container, you specified. #DOCKER REMOVE CONTAINER ALL DOWNLOAD#
If no local image can be found docker run automatically tries to download the image from Docker hub.
docker run Run a docker container based on an image, i. docker images or docker image ls shows all local storage images. creates a container and stores the image under the given name to build a container based on the Dockerfile in the current directory (the dot). docker build is used to build your own container based on a Dockerfile. Link to the docker image is always shown on the right at dockerhub. docker pull download a image from Docker Hub registry. docker ps -a list all container including stopped container. #DOCKER REMOVE CONTAINER ALL CODE#
Whenever you build your own container or you want to timestamp the container you’re using and worked with your applications – check the free timestamping service: Timestamp service for code and container Top 16 docker commands Therefore we decided to create our own docker commands cheat sheet and share it with you. No matter if you’re just getting started with docker or you’re already a professional, there are situations when you can’t remember the correct command or you’re just confused by the order of parameters.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
